Responding to an Emergency (Primary Care)
In all Emergency First Response courses you learn to provide emergency care based on the same priorities used by medical professionals. When someone needs emergency care, time is critical because the chances of recovery get less with time. In most cases you should immediately activate the Emergency Medical Services (EMS) in Thailand by calling 191 or 1669.
Call First - Alert EMS when someone is unresponsive and not breathing normally.
Give Care First - Give care for up to two minutes if you are alone and the patient is not breathing due to drowning or a recognised respiratory problem. Then Call EMS.
Recognising Common Life-threatening Emergencies
Common reasons that cause people to stop breathing;
- Drug overdose
- Heart attack
- Sudden cardiac arrest
- Submersion or Drowning
- Stroke
- Airway obstruction/choking
- Severe Asthma
Helping Others in Need
Some reasons that people hesitate to provide emergency care include;
- Anxiety/Guilt
- Fear of infection
- Fear of making a person worse
- Fear of being sued
The general guidelines of the "Good Samaritan Law" include;
Benefits of assisting someone who needs emergency care include;
- You can save a life
- You can reduce their recovery time
- You could lessen the risk of a permanent disability
The Chain of Survival links between the public and the professionals are represented by;
AB-CABS
AHA Primary Assessment & Cycle of Care [Assess for danger/Apply barriers/Ask for permission/Alert EMS]
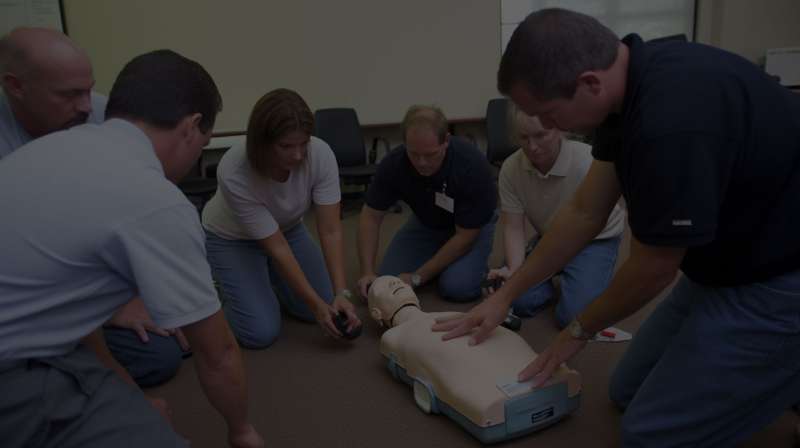
CPR Facts
AED Facts
Common Life-threatening Emergencies
Serious Bleeding Wounds
Place a barrier (rubber gloves/ventilation mask) between your skin and the patient's blood or body fluids to help avoid infection from blood-borne pathogens (hepatitis/hiv). Arterial bleeding produces bright red blood which spurts in rhythm with heartbeats Venous bleeding is dark red and does not spurt from the wound Capillary bleeding oozes slowly from the wound
Important - The primary treatment for severe bleeding is to apply sustained direct pressure on the wound and elevate the injury above the heart if possible. Clean dressings should not be removed from the wound even if the bandage becomes soaked with blood. Place another clean dressing and more pressure on the wound.
Shock Management
Patients often suffer from shock following a trauma and indications include;
- Rapid weak pulse
- Pale bluish tissue colour
- Moist clammy skin/shivering
- Mental confusion/restlessness
- Altered consciousness
- Lacklustre dazed eyes
- Shallow laboured breathing
- Dehydration
- Shock management usually means maintaining normal body temperature for the patient, slightly elevating their legs and feet (if no spinal injury), and monitoring their breathing.
Spinal Injury Management
Common causes of spinal injuries include;
- Traffic accidents
- Falling from a height
- Lightning Strike
- Penetration wounds
- Severe blow to head, neck, or back
- Diving into shallow pools
Indications that someone may have a spinal injury include;
- Headache
- Difficulty breathing
- Vision problems
- Vomiting
- Inability to move a body part/numbness
- Fainting/loss of balance
- Pain in the back or neck area
- *Never move someone with a suspected spinal injury unless absolutely necessary (e.g. Fire/Flood/Unstable building/Roadway). Use the log roll technique if you need to turn them on to their back (e.g. to administer CPR).
Secondary Care - First Aid for non life-threatening injury or illness
Always perform a responsiveness check (primary assessment) using AB-CABS before you perform your secondary assessment. You recognise an injury or an illness using signs (something you can see or hear) and symptoms (something the patient tells you).
STOP your assessment if the patient complains of head, neck, or back pain, otherwise you may treat non life-threatening injuries or common medical illnesses while waiting for EMS.
Injury Assessment [Evaluation from head to toe/provide bandaging or splinting for common injuries]
An Injury is defined as physical harm to the body (examples include bone fracture, dislocation, bruise)
Illness Assessment [SAMPLE]
An Illness is defined as an unhealthy condition of the body (examples include diabetes, asthma, epilepsy)
If in doubt always seek medical attention.

Share on social media